Different Stages of Gum Disease
Two main stages
1. Gingivitis
Gingivitis is early stage of gum disease and potentially reversible through meticulous cleaning. It occurs when dental plaque builds up on teeth, especially where the gum joins the tooth. The signs of gingivitis are bleeding, redness and swelling of the gum.
2. Periodontitis
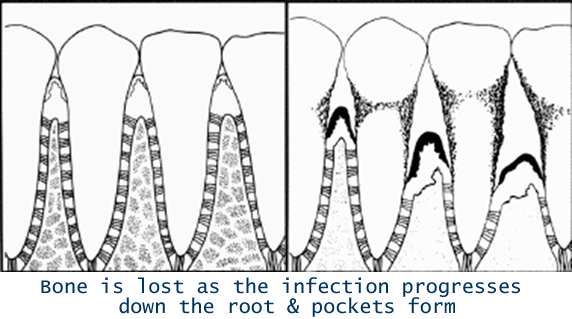
Periodontitis is the advanced stage of gum disease and occurs when gingivitis is not treated. Over time the gum infection causes inflammation in the gum and bone that support the teeth causing it to slowly disappear. As the gum disease progresses, bone loss occurs. This results in spaces between the tooth and the gum. Teeth can become loose, fall out or require extraction.
THE SPACES BETWEEN THE TOOTH AND GUM ARE CALLED PERIODONTAL POCKETS.
Treatment of Gum Disease
The aim is to control the active gum infection and then through regular recall appointments monitor for signs of gum disease activity.
Once susceptible to gum disease, it is important to have regular cleaning and monitoring for the rest of the Patient’s life.
The aim is to prevent further bone loss. By preserving the bone, we keep the teeth for as long as possible.
Treatment involves one or several appointments to remove the plaque and tartar. The severity of the gum disease determines the number of appointments for cleaning or “scaling and root planning” which will be required.
Regularly attending for recall visits is vital to managing the gum disease long term. Frequent recall cleaning appointments allow early removal of the bacteria and allow monitoring of the gum disease activity.
Gum Disease Prevention
Brush your teeth at least twice a day
Clean between your teeth with Floss or Interdentals daily
Regularly 4-6 month professional cleaning at the Dentist
Eat A Balanced Diet
Quit Smoking